I. Overview
1 Current methods of cell culture and observation
Since the 19th century, when the microscope appeared, people began to experiment with cell structure and developed cell culture techniques in the twentieth century. The culture of single-layer cells is relatively convenient, and the commercial microscope is very suitable for the observation of flat and thin samples. Therefore, in the middle and late 20th century, 2D cell culture methods were widely used for biological research, and Conduct research on drug screening, development, and disease treatment.
2 2D and 3D cell culture and effects on cells
In general, 2D cell culture is used not only to study different types of cells in vitro, but also to perform various aspects such as screening and evaluation of drugs. This single layer culture system allows cells to grow on the surface of polyester or glass while the culture medium present provides nutrients for cell growth. In this way, countless biologists have greatly advanced the advancement of biology and medicine.
However, its simple method of operation also causes this model to fail to accurately describe and simulate the complex microenvironment of cells in the body and various complex biological processes such as cell signaling, biochemical processes or geometric changes. In addition, the data obtained by 2D cell culture methods can be misleading and unpredictable in vivo. These reasons have prompted many scientists to turn their attention to 3D cell culture technology, a method that can more accurately describe the true microenvironment of cells in vitro. Cells grow in vitro in a three-dimensional environment to produce specific biophysical and biomechanical signals that affect cell function, such as cell migration, cell adhesion, proliferation, and gene expression (see image below).

We know that there are many different methods of 3D cell culture, and different methods have their own advantages and disadvantages. Unlike 2D culture, 3D cell culture has the formation of tiny structures and complex environmental characteristics that promote cell differentiation and tissue formation. In fact, cells can withstand more morphological and physiological changes in a 3D environment than in a 2D environment. Studies have found that the composition and structure of cell bases can not only affect gene expression, but also enhance cell-to-cell connections. For example, some genes that promote cell proliferation are inhibited in a 3D culture environment, so that they do not grow indefinitely as in 2D culture. 3D cell culture also promotes the growth of two different cell populations in a co-culture environment, enabling accurate reproducibility of tissue function. In addition, 3D culture technology enables cell microenvironment parameters (temperature, compound concentration, oxygen, pH, etc.) to be easily controlled and monitored.
However, 3D cell culture technology also has obvious defects, and these defects require technical advancement to make up for it. First, some matrigel can absorb harmful or unwanted substances, such as viruses, soluble factors, etc. from animals or other sources, which can interfere with cell culture. Some matrices have good cell adhesion, making the cell removal process more difficult. In addition, 3D cell culture technology is a cost-effective technology that eliminates the animal drug testing process during the drug evaluation phase. The entire process can be automated and repeatable.
3 Extension and prospects of 3D cell technology
With the development and maturity of 3D cell culture technology, a large number of new related technologies have emerged, such as microfluidic technology and micro-organ technology. These technologies make it easier to control and monitor the culture environment, and at the same time, the speed at which the drug advances into the clinic is greatly accelerated, and the reliability of the evaluation results is greatly increased.
Second, 3D cell ball culture method
Based on cell growth in 3D cell culture, there are two methods, Scaffold Matrigel-based (SCAFFOLD-BASED) 3D cell culture and substrate-free (SCAFFOLD-FREE) 3D cell culture.
1 type of matrix
The matrix is ​​an important component of 3D cell culture, and different substrates are selected according to different culture conditions and purposes.
2 Scaffold Matrigel-based (SCAFFOLD-BASED) 3D cell culture method
The matrix provides support for cells in cell culture. The cells are able to proliferate and migrate into the interior of the matrix network and eventually adhere to the matrix. As the cells grow, the mature cells interact with each other and eventually form micro-structures that are close to the cell-derived tissue. In most cases, these cells will behave as spheres of varying sizes, called cell spheres: these cell structures are commonly used for drug screening, evaluation, or other 3D cell applications. In general, cell spheres obtained by matrix-supported 3D cell culture methods are larger in size than the cell spheres obtained without matrix support because the matrix provides a larger contact area.
2.1 Types and components of the matrix
The properties and shape of the matrix protein fibers should be compatible with the type of cell cultured. The layout of the matrix protein fibers should be consistent with the simulated organ structure, with similar structures, scales and functions. However, the larger the matrix fibers and the more complex the structure, the more difficult it is to extract. In addition, in order to prevent any possible obstacles (immune response, fibrosis, growth), the substrate used must support cell growth and be biocompatible regardless of the type of matrix used. The matrix can be a hydrogel, a film (or tubular), and a 3D matrix structure.
2.2 Hydrogel matrix
Gels have very good mechanical properties and are the most commonly used substrates. It has a tissue-like rigidity that mimics the effects of the extracellular matrix to some extent. In fact, like other matrices, the hollow structure of gel is like an extracellular matrix that maintains nutrients and soluble factors (such as cytokines, growth factors). These soluble factors are produced by cells and spread in gels. To enable cells to communicate via indirect contact. In this way, it is very suitable for the simulation of microcellular solid tissues, and on the basis of this, the toxicity detection and evaluation of drugs are carried out.
Contains a large amount of water and natural biomolecules (alginate, gelatin, hyaluronic acid, agarose, laminin, fibrin) as a matrix. However, its gelled matrix is ​​complex and makes preparation and handling very difficult.
Synthetic and natural biopolymers are also available as 3D cultured gels. A variety of different polymers can be found, including inert and biodegradable, depending on the experimental conditions and ultimate purpose. The polymer is easy to handle and is more suitable for building substrates.
Other types of substrates: In addition to hydrogels, many matrix materials are available. Non-gel polymeric matrix materials are commonly used in tissue engineering, and different materials need to conform to the mechanical and physical characteristics of the organ to be simulated.
3 3D cell culture without matrix (SCAFFOLD-FREE)
To form a cell sphere, a cell mass can serve as a good physiological module without relying on solid material support. The cell spheres thus obtained are usually relatively small and relatively loose. The most important scaffold-free 3D cell culture methods are forced-floating, hanging drop and agitation based.
The forced-floating method is carried out using a perforated plate coated with an ultra-low adhesion polymer. It was obtained by adding a cell suspension to the well and then centrifuging.
The hanging drop method is a process of concentrating cells into compact, uniform cell spheres by treating the droplets containing the cells.
Agitation based Use a bioreactor to obtain a three-dimensional cell structure.
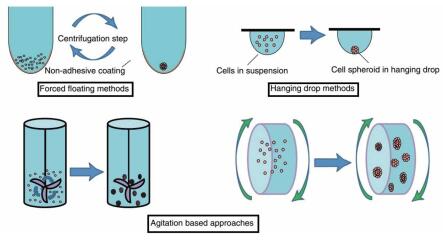
The forced-floating method is simple to use and suitable for batch acquisition and is widely used. There are many different products on the market that can be used to obtain 3D cell spheres simply and quickly.
3.1 Uniform cell ball
The homogenized cell sphere is a cell sphere obtained using a porous plate such as a Cell-able Oncology. The plate uses photolithography to obtain a uniform size of voids on the surface of the porous plate, and the suspended cells can adhere to the holes to grow into spheres.
The cell sphere obtained by this method has uniform size and consistency. At the same time, there are a plurality of micropores in each well to form a plurality of cell spheres, which can obtain a large number of cell spheres at once (equivalent to repetition), and is suitable for large-flux and large-scale detection.

3.2 Ultra-low adhesion U-shaped porous plate
The cell suspension is added to the ultra-low adhesion U-bottom multi-well plate, and after standing culture for 2-4 days, a uniform cell structure with a uniform size is formed.
The method is simple in operation, easy to enlarge, cheap in consumption, convenient for treatment of different drugs, and is very suitable for toxicity evaluation and drug screening of drugs.

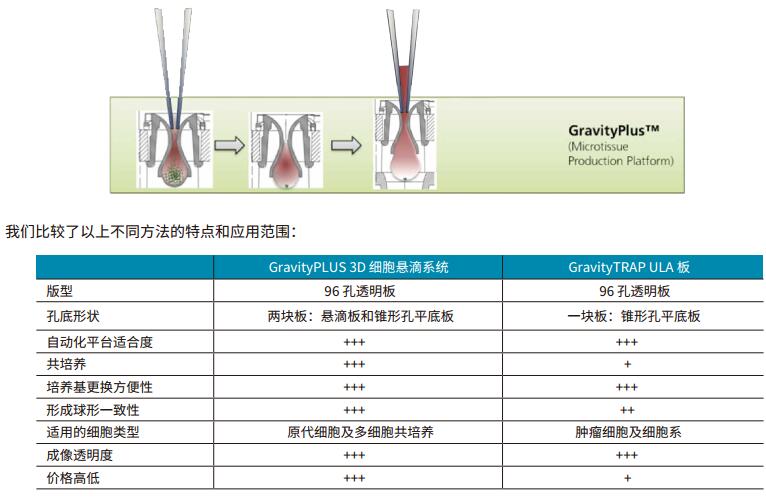
3.3 GravityTRAP microsphere method
The GravityTRAP method is a special design that utilizes this consumable in a form similar to a perforated plate, but at the bottom is a consumable that is extremely limited in area. This method is similar to the droplet method in that a uniform cell sphere can be obtained. But only for some types of cells (see table below).

However, the operation of this method is not convenient (manual addition of cell suspension), consumables are relatively expensive, and to a certain extent limit its role in drug screening and evaluation.
3.4 GravityPlus
GravityPlus is a method in which the cell ball is obtained by hanging drop method, and the cell suspension is injected into the hole. Due to the surface tension of the liquid, a drooping droplet is formed below the hole, and the cells in the droplet gradually form a cell ball due to gravity.
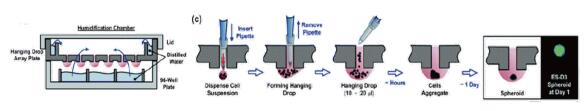
3.5 Hanging drop plate
Uniform cell spheres can be obtained using a conventional droplet method using a responsive gravity-suspended multi-well plate.
High-content imaging detection technology for 3D cell spheres
According to the purpose of 3D cell ball detection, different imaging methods are adopted to achieve the experimental purpose efficiently and conveniently.
1 transmitted light imaging
Transmission of light imaging of 3D cell spheres with high content is a common method. Through the imaging of transmitted light, the shape and size of the cell sphere can be observed as a whole, and the detection of apoptosis and growth inhibition can be conveniently performed. With the help of high-intensity image analysis, cell ball recognition, cell size measurement, and cell ball cell count can be easily and easily determined.

2 fluorescence imaging
2.1 Wide field fluorescence imaging technology
Utilizing wide field fluorescence imaging technology, it is possible to accurately measure and judge apoptosis in cell spheres by using various fluorescent kits, and to accurately measure intracellular expression by antibody labeling technology. For wide-field fluorescence imaging, since the focal plane image is subject to fluorescence interference from the non-focal plane, accurate cell numbers are generally not available (approximate calculations only by the area of ​​the fluorescence-positive area). In addition, there is a lack of resolving power for cells of different Z levels, resulting in large deviations in results.
Wide field fluorescence imaging technology and transmitted light imaging technology can be combined at the same time to achieve the above functions simultaneously.

2.2 Confocal imaging technology
The use of a high-connotation system with confocal function not only enables a clearer image of the cell sphere, but also the image inside the cell sphere. By confocal imaging, images of any level in the cell sphere can be obtained, and very accurate cell quantitative information, including cell number, apoptosis, protein expression, protein distribution, etc., can be obtained, unlike wide field fluorescence imaging and transmitted light imaging. Only the overall information of the cell sphere can be obtained.
3 3D cell sphere analysis technology
3.1 The purpose and significance of 3D cell ball analysis
3D cell ball technology is a very promising technology for biological research, drug screening and drug evaluation. Due to its ability to be quantified and scaled, most of the new related technologies are used for tumor treatment research, most of which are used for drug screening and evaluation. For the screening and evaluation of drugs, quantification of cell ball changes (morphology and function) under different interventions/drugs is of great significance for drug research, with high accuracy and non-offset on cell spheres and cell spheres. The quantification of cells becomes very important, which not only affects the results of drug screening, but also plays a key role in distinguishing the efficacy or effects of different Hits, especially the in vitro accurate evaluation of tumor personalized treatment effects.
3.2 2D analysis method
3.2.1. Implementation of the 2D analysis method
As a three-dimensional structure, the cell sphere can indirectly reflect the characteristics of the three-dimensional structure through its two-dimensional projection or two-dimensional results. For wide field fluorescence imaging and brightfield imaging, due to its weak Z-axis resolution, it is often difficult to perform 3D reconstruction and analysis directly, but mainly for two-dimensional analysis. Of course, there are a variety of 3D deconvolution algorithms, such as the 3D deconvolution blind algorithm provided by AutoQuant, Huygens, etc., which can greatly improve the Z-axis resolution of wide-field fluorescence. The results can be analyzed in three dimensions. .
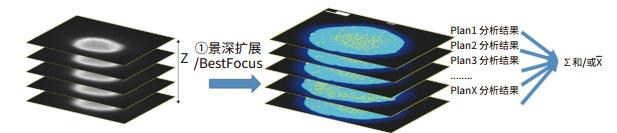
To obtain a two-dimensional projection image, a Z-sequence of the cell sphere is required to obtain a two-dimensional final projection image.

As shown in the above figure, after Z-sequence imaging of each layer position of the cell sphere, after obtaining the depth of field expansion or Best Focus processing on the obtained Z-sequence image, a high-quality 2D projection image of the 3D cell sphere can be obtained. The Z-sequence image usually does not use the Maximal Projection method, because it will cause the background signal to accumulate, reduce the signal-to-noise ratio of the final 2D projection image, and ultimately affect the analysis result. The obtained 2D projection image can be quantitatively analyzed for 3D cell spheres using conventional 2D analysis methods.
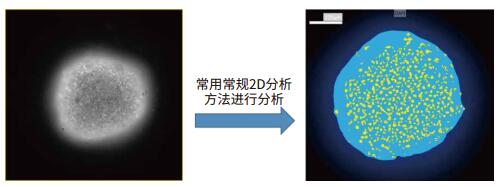
For confocal imaging systems, since the system itself provides high Z-axis resolution, each 2D image obtained can be averaged/summed by 2D analysis of each image of the Z-sequence image. Reflects information about the 3D structure.
3.2.2. Defects in the 2D analysis method
2D is a projection or subset of 3D. Therefore, when the Z-sequence image of the 3D cell is obtained by confocal or 3D deconvolution, and the 3D internal information of the cell sphere is obtained, the result obtained by the 2D method can only understand the information of a 3D structure from a single perspective. And can't get the whole picture. Because 2D is only a subset of 3D, the 2D results will vary greatly depending on the method (see the image below):
(1) Using 2D projection will result in significantly lower results
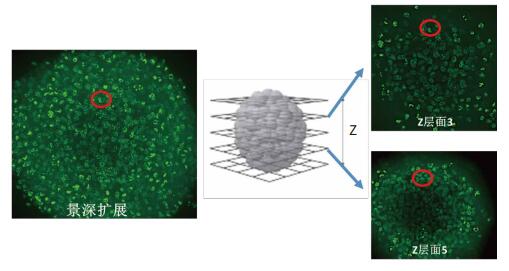
On the right is the 3D cell sphere Z-axis scan of two of these layers. Where level 3 and level 5 have cells at the same position in the image (red circle), that is, cells above and below the same position, these cells are similar to the same cell in the depth-of-field image, resulting in The cell count results obtained by 2D projection analysis were significantly lower.
(2) The use of stratified summation will result in significantly higher results
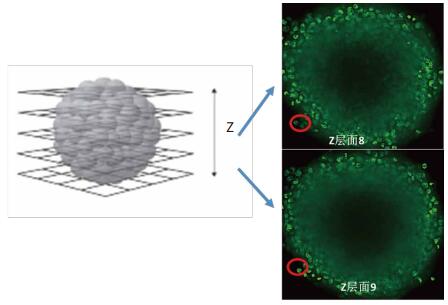
On the right is the 3D cell sphere Z-axis scan of two of these layers. Level 8 and Level 9 both captured the same different level, resulting in a significantly higher cell count result obtained by stratified summation analysis.
(3) When it is necessary to detect spatial information such as the distance and position of different cells, the two methods also cause obvious problems, such as the stratification summation method, which cannot determine the position and distance information; the 2D projection method obtains only one The projection of the plane, the result will be significantly lower or wrong (such as when the cells are stacked up and down)
3.3 3D analysis method
Of course, the information to obtain 3D cell spheres comprehensively and accurately can only be obtained by 3D analysis. The 3D analysis method can automatically reconstruct the 3D cell sphere in three dimensions, and perform quantitative measurement (cell number, size, volume, surface area, etc.) and position information measurement (space distance, position, etc.) in the reconstructed three-dimensional space.
There is now an emerging cytostress that studies tumors by “congestion features†and “phase transitions†of cells in three-dimensional tumor cell spheres and tumor tissues (through contact areas between cells in three-dimensional structures and spatial cell morphology). There has been considerable progress in the study of metastatic matrix of tumor cells.
Fourth, the advantages of ImageXpress Micro family products for 3D cell culture and detection
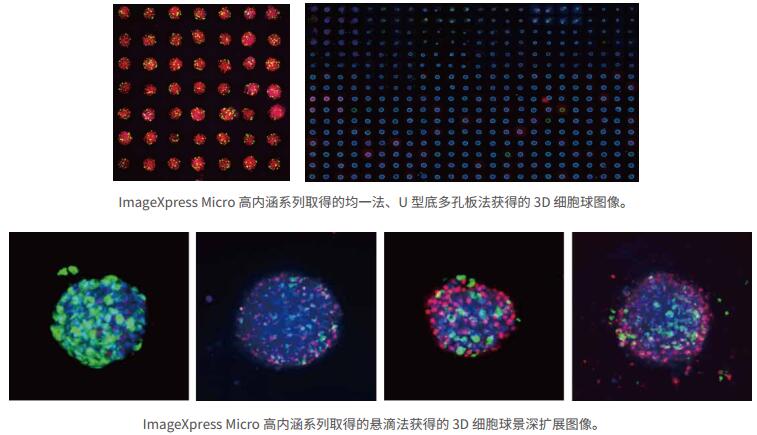
1 can be used in all 3D cell sphere methods
The ImageXpress Micro family of high-content products is highly compatible and scalable, enabling the imaging of all current 3D cell spheres, while supporting new approaches to 3D imaging such as 3D cell microfluidics, 3D micro-organs, etc. Rapid imaging and analysis of experiments. Optimized and perfected for more than 15 years, the laser autofocus system quickly finds the focal plane position of the 3D cell sphere for clear imaging. Laser autofocus combined with image autofocus technology can accurately and quickly find the precise focal plane position of 3D cell spheres under different conditions of different 3D cell spheres and different levitation heights in different wells, achieving fast and accurate cell sphere imaging.
2 Perfect laser auto focus + image auto focus, support various 3D cell ball making methods and future upgrade space for new consumables
The IXM Series High Connotation System's sophisticated and unique laser autofocus system tracks any plane within the sample for fast and precise focusing, enabling accurate positioning of the cell spheres quickly in accordance with the 3D cell plate settings within 0.3 s.
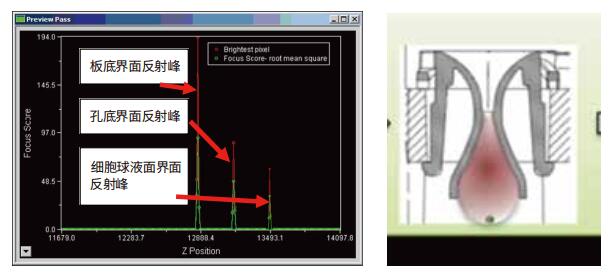
The above is a schematic of rapid laser autofocusing of the 3D cell sphere obtained by the Hanging drop plate. The IMX can automatically obtain the reflected light of multiple interfaces and determine the position of the cell sphere. Because the cell sphere is stably suspended above the liquid surface (surface tension), by confirming the approximate diameter of the cell sphere, the system can quickly and accurately obtain the exact position of the Z-axis of the cell ball through the cell ball surface interface. If the image is set by autofocus, the system can accurately locate any level of the cell sphere after finding the exact position of the Z-axis of the cell sphere.
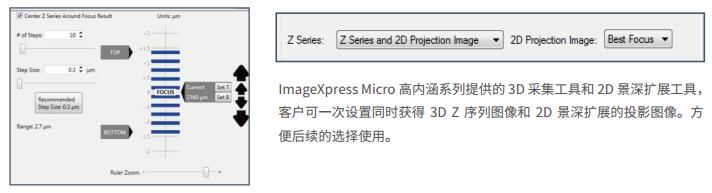
3 Efficient and flexible Z-sequence acquisition saves time and space
The ImageXpress Micro family of products combines efficient and convenient 3D imaging for 3D imaging and 2D imaging of cell spheres. The system provides automated Best Focus depth of field extensions that are available in one setup without the need for follow-up. The flexible features allow for the separate acquisition of 3D Stack images or 2D depth of field extended images, or simultaneous acquisition, allowing customers to balance the need for accurate 3D imaging and 2D depth of field expansion.
4 turntable confocal + 3D deconvolution
ImageXpress Micro Confocal (IXM-C) is a highly flexible and high image quality confocal high content system. It has a variety of confocal turntables for high-throughput and high-resolution imaging. Deconvolution processing based on wide field or confocal imaging to obtain higher resolution and signal to noise ratio images is a common method of biological imaging. The IXM-C has a 3D deconvolution function based on the confocal confocal, and the obtained confocal image itself has excellent Z-axis resolution. By combining the 3D deconvolution function, the resolution in the XYZ direction can be further improved, resulting in sharper image details (above).
5 powerful 3D analysis capabilities
As mentioned earlier, images of 3D cell spheres can be obtained by different 2D recognition analysis, but the defects of 2D analysis are very obvious (see above). Accurate data results for 3D cell ball experiments rely on 3D analysis tools. The ImageXpress Micro high-content system features high-performance 3D analysis tools. The software can automatically identify cells at the three-dimensional level, and automatically perform three-dimensional structural reconstruction, and perform cell identification and analysis in the reconstructed three-dimensional structure.


6 Parallel analysis and calculation
ImageXpress PowerCore is a parallel analysis and calculation function for MD high-content systems that enables the following useful functions:
A: Image analysis is performed synchronously during image acquisition (without affecting image acquisition speed).


B: The time taken for image analysis is greatly accelerated.
When performing 3D imaging and analysis, the number of images obtained and the analysis load are significantly increased due to the need to perform multiple acquisitions of 3D information on different levels of Z-axis images. ImageXpress PowerCore significantly speeds up image analysis, dramatically increases throughput, and provides faster analysis speeds than image acquisition. The following examples visually reflect the power of ImageXpress PowerCore.

7 3D cell ball + cell function test
Conventional somatic cell lines or tumor cell lines are conventional subject cells for 3D cell ball experiments. For some special cells, such as nerve cells, cardiomyocytes, skeletal muscle cells, endocrine cells, their normal physiological characteristics depend on their specific cellular characteristics, such as action potential, local potential changes, ion release and so on. The MD high-content system can not only perform imaging analysis of complex experiments such as 3D, but also the above special cell types such as frequency and speed of action potential change, enabling rapid imaging and characterization.

The neural cells obtained by iCell differentiation grow into a neural network in a small gel medium. By the labeling of the calcium ion reagent, the release of calcium ions due to the action potential on the nerve cells can be seen, indicating that the neural network function is good. The software system automatically recognizes fluorescently labeled cells and automatically analyzes the frequency and magnitude of changes in electrical signals (calcium release).

V. Summary
3D cell ball detection technology will bring more accurate and reliable methods than traditional 2D cell detection methods, and is closer to the results of clinical experiments. Accurate results can greatly reduce the cost and time of drug screening in drug screening. In scientific research, due to its inherent advantages, it can more accurately reflect the biological performance and response of cells. 3D cell ball technology is a basic method. With the development of technology, more specialized methods, such as organ-like, micro-tissue, etc., provide a more powerful weapon for biological research and drug screening.
3D cell ball technology, because of its three-dimensional structure, can only obtain accurate and reliable results through 3D imaging and analysis technology. Molecular Devices' ImageXpress Micro series of high-content systems not only provide all the details and functions of 3D cell technology, including 3D imaging and 3D analysis, which is fully compatible with the 3D cell ball technology consumables currently on the market. Its perfect laser autofocus + image autofocus technology is extremely tolerant and open, enabling the detection and analysis of new consumables and methods in the future. The MetaXpress PowerCore High Connotation Parallel Acceleration Software System dramatically increases system throughput and accelerates drug testing and time and labor costs.
Buckwheat is nutritious and full of treasures. Nutrition experts identified: buckwheat contains 13.1% protein, 17.7% vitamins, 18 kinds of amino acids are complete, and the content of lysine and tryptophan is unmatched by other food crops. Calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, zinc, selenium and other trace elements are complete, especially suitable for hypertension, dyslipidemia, coronary heart disease, diabetes, obesity, arteriosclerosis, loss of appetite, gastrointestinal stagnation, chronic diarrhea and night sweats The first choice for patients. Buckwheat also has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, cough, asthma, and phlegm-relieving effects, so buckwheat is also known as "anti-inflammatory food".
Jilin Yomi Agricultural and Sideline Products Import and Export Co.LTD. focusing on building a green base, building a characteristic industrial chain, deepening the channel supply chain, vigorously developing export trade, and leading the development direction of the entire industry; insisting on green development, promoting the concept of health, and making every effort to build a national leading enterprise in the organic grain industry.
Buckwheat Rice,Buckwheat Quinoa,Buckwheat Rice Nutrition,Buckwheat And Rice
Yomifresh , https://www.yomifresh.com