In recent years, CAR-T is considered to be one of the most promising treatments for cancer because of its great potential in liquid tumors such as leukemia. However, there are still problems such as immunosuppressive microenvironment, weak T cell efficacy and cytotoxicity. It restricts the function of CAR-T. In the first two issues, we have already learned the basics of CAR-T. In this issue, we will introduce some small star molecules that affect T cell function (proliferation and immune function) in CAR-T therapy, such as cytokine IL- 7, IL18, IL-21, IL15 and other effects in tumor immunity. Maybe they can open a new window for the effectiveness of CAR-T.
What is a cytokine?
Cytokine (CK) is a small molecule soluble protein secreted by activated immune cells that mediates and regulates cellular functions (immune response, inflammatory response, hematopoietic function, etc.). According to different functions, it can be divided into several categories such as interleukin, interferon, tumor necrosis factor superfamily, colony stimulating factor, chemokine, and growth factor.
Relationship between cytokines and tumors
In recent years, experimental results have shown that local injection of cytokine IL-2 into the tumor, a large number of granulocytes and macrophages are recruited to the tumor area or even penetrate into the tumor, resulting in a strong anti-tumor effect, and ultimately tumor regression. In addition, some other cytokines such as IFN-α, GMCSF, etc. can also induce tumor cell death, suggesting that CK has broad application prospects in the field of anti-tumor.
What is the relationship between cytokines and CAR-T?
At present, the development of tumor immunotherapy CAR-T is in full swing, but there are still obstacles, such as short life span of T cells and insufficient efficacy. These problems have seriously hindered the efficacy of CAR-T in curing tumors, especially in the treatment of solid tumors. In view of the anti-tumor function of cytokines, it is not difficult to imagine that co-expression of these cytokines will solve this problem and is expected to become an important means to overcome solid tumors.
For example, the fourth generation of CAR-T: the ability to express some key cytokines on the basis of the second/third generation CAR-T shows the ability to overcome the microenvironment of the solid tumor immunosuppression.
Taking IL-12 as an example, systemic injection of IL-12 causes severe inflammatory side effects, but after local expression is achieved by fourth-generation CAR-T cells co-expressing IL-12, NK cells can be recruited at tumor lesions. Or directly reverse the depleted tumor infiltrating T lymphocytes, thereby effectively overcoming the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment. Other studies have found that co-expression of certain chemokines in CAR-T cells can also enhance the homing ability of CAR-T cells.
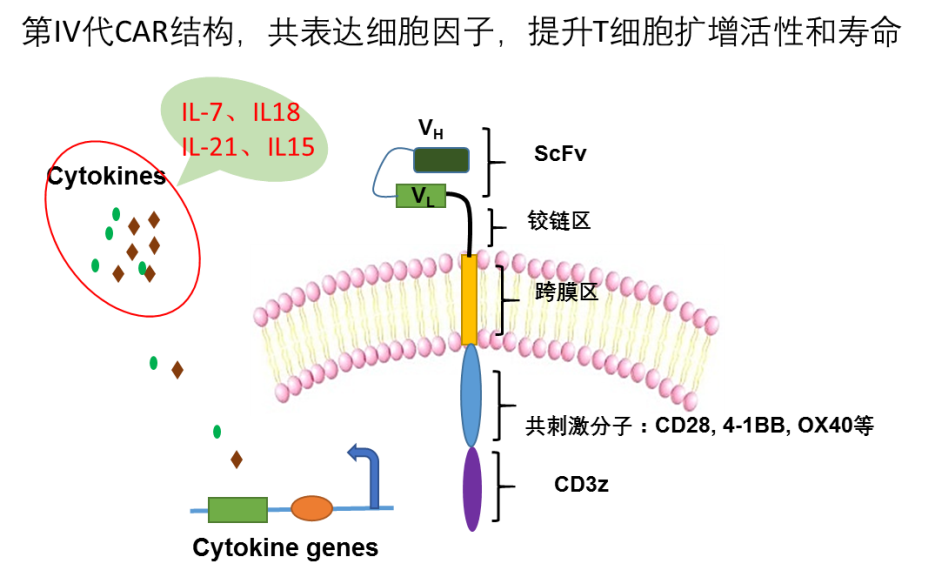
Therefore, attempts to co-express cytokines with important immunomodulatory capacity in CAR-T cells, such as IL-7, IL18, IL-21, IL15 and other cytokines, are likely to greatly enhance the activity of T cells.
In this issue, we will introduce the function of cytokine IL-7 and its relationship with tumor immunity.
Human interleukin-7 (IL7) is a pleiotropic cytokine with a wide range of immune effects. For a long time, the understanding of IL-7 has been affecting the growth, survival and differentiation of B cells and T cells [1]. However, in recent years, some studies have shown that IL-7 has a direct or indirect effect on anti-tumor. Let's take a look at the discovery, function and application of IL-7.
Discovery of IL-7 In 1987, Hunt et al. found in the experiment that in 1988, Namen et al purified and cloned it, named lymphopoietin-1, and was named interleukin-7 in the same year. The classical signaling pathway mediated by IL-7/IL-7R is shown in Figure 1 below [4]:

What is the relationship between IL-7 and T cells?
1. Regulate the development of T cells
T cells are regulated by IL-7Rα expression during thymic development. IL-7Rα expression can also be re-induced under TCR-mediated. As shown in the figure: IL7/7R regulates the development of T cells. The TCR signal persists, the IL-7R signal is blocked, and differentiates into CD4+ single positive T cells; the termination of TCR signaling, IL-7R signaling, and differentiation into CD8+ single positive T cells [5].
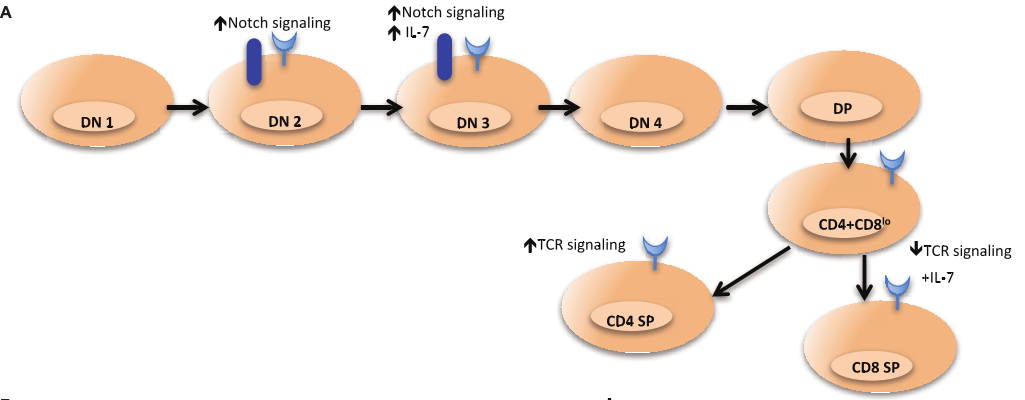
2. Promote the proliferation of T cells
The study found that IL-7 expression is closely related to T cell proliferation. If IL-7 is used to stimulate fresh T cells, T cells can be dose-dependently amplified, including CD4+ and CD8+ subpopulations; knockout of IL-7R, T cells will stop growing; transfer of IL-7 gene can promote CD4+/ CD8+ Proliferation of T cells. However, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells have different responses to IL-7. IL-7 has a stronger effect on CD8+ T cell subsets than CD4+ cell subsets [6, 7].
As shown in the figure below, Lisa A et al. explored whether IL-7-activated T cells are involved in the induction of proliferation. By injecting IL-7 into mice, it is possible to induce T cell proliferation in an activated state, and the longer the administration time, the multiple of proliferation. The larger the IL-7 injection time is greater than 4 days, the CD8+ T cell subsets are more proliferative than the CD4+ cell subset.

3. Prolong the survival time of memory T cells
IL-7Rα is selectively expressed in a small fraction of effector T cells in the primary immune response and then converted to central memory T cells. And IL-7 is particularly important for the survival of memory T cells. In lymphopenia, the effect of IL-15 on memory T cells can be replaced by IL-7 [8].
4. Anti-tumor effect
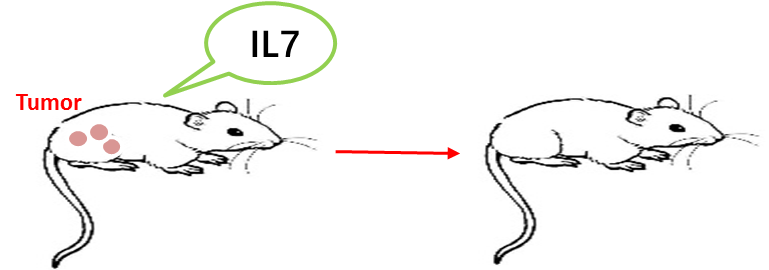
As early as 1994, McBride et al. injected recombinant human IL-7 into the tumor basal part of human fibrosarcoma mice, and found that IL-7 can inhibit tumor growth and even completely eliminate some mouse lumps [9]! ! ! This is because the recombinant human IL-7 intraperitoneal administration can increase the leukocytosis in the spleen and lymph nodes of normal or tumor-bearing mice, indicating that exogenous injection of IL-7 can induce the body's anti-tumor immune mechanism.
David H. Lynch et al. participate in immunization by specifically targeting anti-tumor CTL cells (cytotoxic T lymphocytes, a specific T cell, specifically secreting various cytokines; killing certain antigens, tumor cells and other antigenic substances). Effect), IL-2/4/7 was added to the medium to investigate the effects of these three cytokines on the anti-tumor ability of CTL cells. The results showed that IL7 was the most effective; alone or in combination with low doses of IL2, CTL amplification capacity was enhanced 6-8 times; while only IL7 was added, the anti-tumor ability was 4 times stronger than the control group; IL4 or IL2 was added alone. In combination, the anti-tumor ability was less than 4 times that of the control group [10].
What are the clinical applications of IL-7?
The potent immune effect of IL-7, especially the function of regulating T cell proliferation, maintaining its intracellular environment stability, and enhancing the immune response of T, makes IL-7 more and more an immune regulator. Having attention.
At present, the application of IL-7 to immunotherapy has entered the clinical stage and achieved certain effects, including melanoma and lymphoma, cervical cancer, colon cancer and the like.
For example, Möller et al. modified the autologous tumor vaccine by IL-7 and injected it into patients with malignant melanoma by subcutaneous injection. All patients were found to be resistant to tumor vaccine with few side effects. Eight of the patients were immunologically monitored and found a significant increase in the number of killer T cells. Only 2 of them developed hypothermia and mild flu-like symptoms 1 day after vaccination.
The current clinical data consistently demonstrate that IL7 has a strong ability to amplify initial T cells and anti-tumor. And its side effects are few and patients can tolerate it. This provides an opportunity for IL-7 to be used in cancer therapy.
In summary, I look forward to the application prospect of IL-7 for tumor therapy.
1 Preparation of fourth generation CAR-T cells. Traditional second-generation and third-generation CAR-T cells have shorter survival time and weaker amplification ability in vivo. Co-expression of IL-7 can prolong the survival time of CAR-T cells and increase the ability to expand and kill tumors;
2 to prepare more powerful immune performance of the tumor vaccine. Transfection of IL-7 with other growth factors (such as B7) can increase the immunogenicity of the tumor cells, thereby inducing a stronger anti-tumor effect;
3IL-7 is used in combination with other cytokines. IL-2 is currently recognized as one of the most potent anti-tumor cytokines, but the clinical application of toxic side effects is large, IL-7 side effects are less, so the IL-2 dosage can be reduced to reduce side effects.
In summary, IL-7 plays a huge role in tumor immunity, such as regulating T cell proliferation, maintaining its intracellular environment stability, and enhancing the ability of T immune response. I believe that if IL-7 is properly involved In tumor immunity, such as co-expression to CAR-T, may give CAR-T a different anti-tumor effect, let us wait and see.
references:
[1].Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones..
[2].Reconstitution of a functional interleukin (1L)-7 receptor demonstrates that the IL-2 receptor y chain is required for IL-7 signal transduction.
[3]. Carrette, F. and CD Surh, IL-7 signaling and CD127 receptor regulation in the control of T cell homeostasis. Seminars in Immunology, 2012. 24(3): p. 209-217.
[4]. Nguyen, V., A. Mendelsohn and JW Larrick, Interleukin-7 and Immunosenescence. Journal of Immunology Research, 2017. 2017: p. 1-17.
[5].Heritable Gene Regulation in the CD4 CD8 T Cell Lineage Choice.
[6]. Human IL-7: a novel T cell growth factor..
[7]. Geiselhart, LA, et al., IL-7 Administration Alters the CD4: CD8 Ratio, Increases T Cell Numbers, and Increases T Cell Function in the Absence of Activation. The Journal of Immunology, 2001. 166(5) : p. 3019-3027.
[8]. Interleukin-7 mediates the homeostasis of naïve and memory CD8 T cells in vivo.
[9].Administration of recombinant human IL-7 to mice alters the composition of B-lineage cells and T cell subsets, enhances T cell function, and induces regression of established metastases..
[10]. In vivo evaluation of the effects of interleukins 2, 4 and 7 on enhancing the immunotherapeutic efficacy of antitumor cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
Nuts are a group of cleistoses that have a hard skin and contain a single seed. It is the essence of plants, rich in nutrition, containing higher minerals, vitamins, oil and protein, eating more can promote growth and development, increase physical fitness. Common nuts include walnuts, peanuts, almonds, cashews, macadamia nuts, pistachio nuts and so on.
Nuts, Almonds,Walnuts,Pistachio nuts,Macadamia nuts
Xi'an Gawen Biotechnology Co., Ltd , https://www.seoagolyn.com