[Classical literature review] The philosophical monologue of exFoxp3 Th17 cells
"Who am I? Where do I come from? Where do I go?" It is Plato's three classic questions about classic philosophy. Xiaobian uses this question to wake up my sleeping soul every morning before getting up. In the classic literature review brought in this issue, please follow the author of this article to listen to the profound philosophical monologue of ex Foxp3 TH17 cells!
Autoimmune diseases are usually caused by imbalance between regulatory T cells (Treg cells) and helper T cells (TH17 cells) that produce interferon 17, which seriously affect human health. However, the source of TH17 cells is still unknown, so the monologue of the protagonist ex Foxp3 TH17 cells began in autoimmune arthritis.
First, where do I come from?
exFoxp3 T H 17 cells Tuosai depressed thinking: I, as a T H 17 cells, the feeling of T H 17 cells with other small children who are not particularly gregarious partner, often have a different feeling, I come from?

Let me start from the beginning and look for key people who influence autoimmune arthritis: Treg cells expressing Foxp3 are already known to be a key player in suppressing immune responses. Deletion of Foxp3 in mice produces autoimmune diseases that persist. Inhibition of autoimmunity, the stability of Foxp3 expression is an important factor in the balance between the two.
So what is the effect of Foxp3 stability on autoimmune arthritis? The development and function of Treg cells are regulated by IL-2, which consists of Foxp3+-stabilized CD25 (IL-2Rα)hi and Foxp3+-unstable CD25lo cell populations. The authors transferred CD25hiFoxp3+CD4+ cells and CD25loFoxp3+CD4+ cells (derived from untreated DBA/1 Foxp3hCD2 mice, hCD2 as a tag to indicate Foxp3 expression ) to a small collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) disease model. In the mouse, the clinical score and ankle injury were measured, and it was found that CD25hiFoxp3+CD4+ cells reduced symptoms such as joint swelling and injury compared with the control group and CD25loFoxp3+CD4+ cells (Fig. 1a, b). The cells were labeled with CFSE dye and then transferred, and the results showed that CD25loFoxp3+CD4+ cells lost part of Foxp3 expression (30-50%) in spleen and draining lymph nodes (dLNs) (Fig. 1c). Thus, CD25 lo Foxp3 + CD4 + cells have no way to alleviate the symptoms of inflammation and bone damage due to the loss of Foxp3. Thinking about it, I couldn't help but ask: Where did the CD25 lo Foxp3 + CD4 + cells of Foxp3 be lost ?
Don't worry, we continue to track the development of cells for a longer period of time, transferring total Foxp3 + , CD25hiFoxp3 + CD4 + and CD25loFoxp3 + CD4 + cells (derived from B6.Ly5.1 Foxp3hCD2 mice, donor) to C57BL/6 Ly5.2 arthritis In the mouse model, Foxp3 and IL17 expression was detected, and CD25loFoxp3+CD4+ cells lost part of Foxp3 expression, resulting in higher IL-17 (Fig. 1d, e). It was also detected that Ly5+Foxp3-CD4+ T cells derived from CD25loFoxp3+ had more IL-17 and CCR6 expression than naïve CD4+ T cells (both TH17 cell markers). This is clear. It turns out that these CD25 lo Foxp3 + CD4 + cells have become my (exFoxp3 TH17 cells) after losing Foxp3 . I have differentiated from CD25 lo Foxp3 + CD4 + cells.

Figure 1. CD25loFoxp3+ T cells are unstable Foxp3 + T cells that convert to T H 17 cells under arthritic conditions.
Second, who am I?
It turns out that I came from CD25loFoxp3+CD4+ cells. Who am I? Who is my ancestor?
CD25loFoxp3+CD4+ cells lose Foxp3 to exFoxp3 T cells, then is my ancestor an exFoxp3 T cell? Then take a look at the exFoxp3 T cells.
The reporters of the Biotech series have mentioned the tracer effect of fluorescent reporter mice. The authors of this experiment used fluorescently labeled Foxp3-GFP-Cre mice to mate with Rosa-loxp-Stop-loxp-YFP mice, GFP. - indicates Foxp3 - cells, GFP + indicates that cells are expressing Foxp3, after GFP expression, while crease expression binds to loxp site to remove stop, YFP fluorescence is expressed, but if it is lost immediately after Foxp3 expression, GFP of this part of cells It becomes negative and YFP is still expressed. Therefore, YFP + indicates that Foxp3 is being expressed or has been expressed [2-3] . According to the fluorescence expression, it can be found that GFP - YFP + cells (exFoxp3 T cells) account for the proportion of CD4 + T cells in the mouse model of arthritis, and the joints are higher than the lymphoid organs and selectively accumulate at the joint synovium ( Figure 2a). Compared to GFP - YFP - cells (Foxp3-CD4+ T cells), exFoxp3 cells produced more RANKL (transcription factor kappa B receptor activating factor ligand) and CCR6 molecules (Fig. 2b). IL17-positive exFoxp3 T cells have the highest proportion of inflammatory joints (Fig. 2c). This show that exFoxp3 T cell activation of T H 17 won the phenotype (ex Foxp3 T H 17 cells, this is my friends) and accumulate in the inflamed synovium.
Well, I found my ancestor ex Foxp3 T cells, so let me study which tribe I belong to?
There are three possible sources of exFoxp3 T cells: tTreg cells (thym-derived Treg cells), pTreg cells (peripheral-derived T reg cells), activated traditional T cells (expressing a few moments of Foxp3). Treg cells characteristically express Foxp3 and have specific demethylation regions and express some other marker molecules. The GFP - YFP - Expression and analysis of flow methylation, exFoxp3 T cells, GFP + YFP + cells were part of the molecule. The flow data showed that the expression of GTIR, Nrp1 and KLRG1 was similar in exFoxp3 T cells compared with GFP + YFP + cells, and the expressions of CD25, FR4, OX40, CD39 and CD103 were lower. This indicates that exFoxp3 T cells express more Treg cell markers, which are still different from traditional T cells (Fig. 2d). Which type of Treg cells does it belong to? tTreg cells are known to have their Foxp3 site demethylated. The authors further analyzed the degree of CpG methylation in Foxp3, IL2rα, and Ctla4 sequences. Most of the Foxp3 sequences in exFoxp3 T cells were methylated and the Il2ra portion was methylated (Fig. 2e). This result is different from the known tTreg cell characteristics. In addition, gene expression analysis revealed that exFoxp3 TH17 cells overexpressed the preferential expression of molecules Cxcr5, Ccr8, Rora, Rorc in pTreg cells (please refer to the original supplement for more data); more experiments in this paper indicate that ex Foxp3 T H 17 cells are likely From the pT reg cell subset.
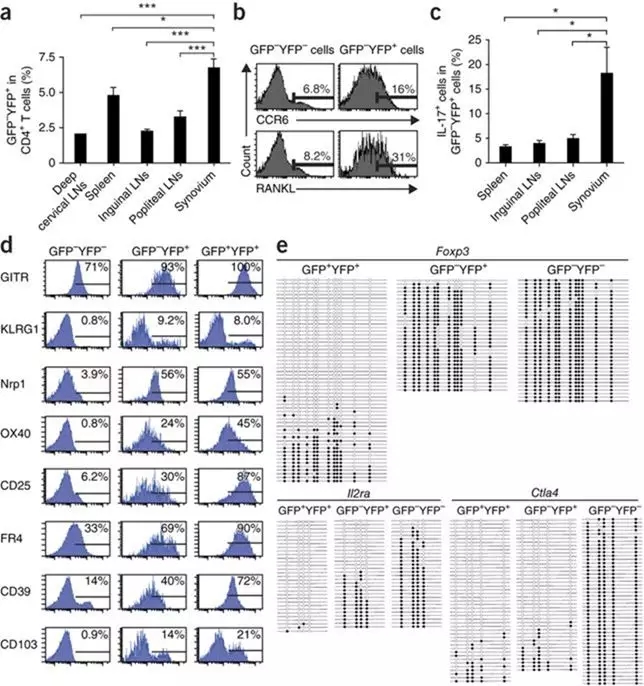
Figure 2. Localization, marker gene expression and DNA methylation status of exFoxp3 T cells in arthritic mice. Results are shown from fate mapping analyses of arthritic Foxp3-GFP-Cre × ROSA26-YFP mice that were performed 2 weeks after secondary immunization.
The third question is how to become me.
Xiaobian: Wait a minute, etc., don’t press the logic, don’t you ask me where I am going?
Me: Go, don't fight, I have more profound questions to think about, how did I become what I am now? This is important for understanding the mechanisms by which arthritis occurs.
The results can be found in the above ex Foxp3 T H 17 cells accumulated in inflammation of the joints, the authors assumed that there are cells Foxp3 + T cell responses with a joint, which is converted to induce T H 17 cells. Design experiments isolated Thy1 + CD11b - cells (synaptic fibroblasts) and Thy1 - CD11b + cells ( synaptic macrophages) and Foxp3 + CD4 + T cells (untreated Foxp3 hCD2 mice) from arthritic mice In the co-culture, Thy1 + CD11b - cells down-regulated Foxp3 expression in Foxp3 + CD4 + T cells (Fig. 3a). Thy1 + CD11b - cells were co - cultured with Foxp3 + CD4 + T cells or naïve CD4 + T cells to detect changes in IL17 + Foxp3 - cell ratio and cytokine expression (IFN-γ, IL-4), and the results showed synovial membrane formation. fibroblast cells upregulate exFoxp3 T so that the level of expression of IL-17, IFN-γ and IL-4 expression has not changed, indicating that synovial fibroblasts induce Foxp3 + T cells are transformed T H 17 cells in the joint. Naïve CD4 + T cells did not contribute to this shift. Further study of the mechanism of this transformation, the separation of Thy1 + CD11b - cells and supernatants co-cultured with Foxp3 + CD4 + T cells were detected separately (Fig. 3d), and it was found that cells could not cause this transformation; detection and analysis The cytokine expression of the supernatant showed that the Thy + CD11b - cell supernatant produced a higher IL-6 factor, and IL-6 expression was further enhanced in the presence of IL-17 (Fig. e). The addition of anti-IL-6 antibody inhibited the production of exFoxp3 + T H 17 cells. It was demonstrated that IL-6 derived from synovial fibroblasts is a key factor in the transformation of Foxp3 + CD4 + T cells into TH 17 cells.
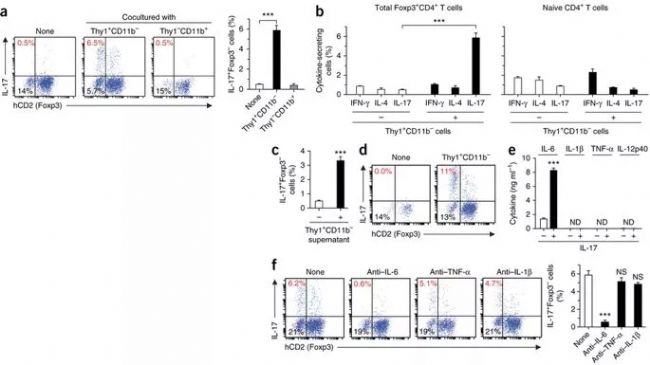
Figure 3. Arthritic synovial fibroblasts promote the conversion of Foxp3 + T cells to T H 17 cells in an IL-6- dependent manner.
The fourth question is what I have high (xie) super (e) ability
Osteoclasts are an important factor in the destruction of arthritic bone. To assess the extent of TH17 cells' effects on bone destruction in arthritis, the authors tested their ability to induce osteoclastogenesis by counting osteoclasts (TRAP-stained multinucleated cells, TRAP + MNs) and RANKL, cytokine expression. Foxp3hCD2 mice were mated with IL-17-GFP mice ( the mice were derived from Biographer ) to facilitate the extraction of IL-17 expressing cells. ExFoxp3 TH17 cells, Foxp3+ T cells, and IL17a -/- TH17 cells were co-cultured with synovial fibroblasts, bone marrow-derived hypertrophy, and macrophage precursor cells (BMMs), respectively. The results showed that exFoxp3 TH17 cells were more potent than TH17 cells (naïve CD4). + T cell derived) has a stronger ability to generate osteoclasts (Fig. 4a, b). The ability of TH17 cells to induce osteoclastogenesis mainly comes from the expression of IL-17. IL-17 can stimulate the expression of RANKL on fibroblasts. Although TH17 cells also produce RANKL, the cells themselves have no way to induce osteoclastogenesis. Deletion of IL-17A expression in IL17a -/- exFoxp3 TH17 cells can still induce osteoclastogenesis, suggesting that T cell-derived RANKL or cytokines, but not IL-17A, have a potential effect on osteoclastogenesis (Fig. 4b). The authors found exFoxp3 TH17 cells ratio of CD4 + T cell-derived naïve of T H 17 cells expressed higher levels of RANKL, through synovial fibroblasts co-culture, RANKL expression is further enhanced. (Fig. 4c)
As shown in Figure 4d, exFoxp3 TH17 cells were co-cultured with BMMs and found that exFoxp3 TH17 cells also have the ability to induce BMMs to form osteoclasts in the absence of synovial fibroblasts. To investigate the effect of RANKL on exFoxp3 TH17 cells and synovial fibroblasts, exFoxp3 TH17 cells were used in co-culture systems (from Lck-cre (T-lymphocyte-specific cre mice) Tnfsf11 (encoding RANKL) flox/Δ Foxp3hCD2 small Synovial fibroblasts isolated from mice) or Tnfsf11 deleted. Results are expressed RANKL expression synovial fibroblasts are the key factors to promote osteoclastogenesis, but not expressed in the presence of synovial fibroblasts of RANKL, exFoxp3 T H 17 cells to promote RANKL expression can be osteoclastogenesis (Fig. 4e, f) .
ExFoxp3 TH17 cells and TH17 cells (naïve CD4 + T cell derived) were analyzed by GeneChip. In contrast, exFoxp3 TH17 cells expressed higher Ccr6, Ccl20, Il23r, Il17re, Tnfrsf21, Vcam1, Rorc and Tnfsf11, lower. Csf2, Tnf, Il10 and Sgk1. The results indicate that exFoxp3 T H 17 cells are not identical to most known pathogenic TH 17 cell subsets and constitute a new subpopulation of pathogenic TH 17 cells .
Look, it's also TH17 cells, I am exFoxp3 TH17 cells, my ancestors are exFoxp3 T cells, which are different from other TH17 cells by obtaining the activation of TH17! (Singing: "We are different." !" )

Figure 4. exFoxp3 T H 17 cells are osteoclastogenic T cells with distinct gene profiles.
Fifth, what are the "contributions" of my family in arthritis?
My ancestors are exFoxp3 T cells from the CD25loFoxp3+CD4+ T cell family. Our family seems to be very powerful. Let's take a look at what they "contribute" to arthritis.
Steady-derived stable Foxp3+CD4+ T cells have a higher affinity for autoantigens and maintain their own tolerance. The authors hypothesized that unstable Foxp3+CD4+ T cells also contain self-reactive T cells and cause arthritis to occur after loss of Foxp3 expression. To investigate the role of autoantigen-specific exFoxp3 T cells, the authors assigned CD25loFoxp3+, CD25hiFoxp3+, Foxp3-, and effector memory CD44hiFoxp3-CD4+ T cells (DBA/1 Foxp3hCD2 mice derived from collagen) to CFSE and transferred to small immunizations. In the murine model, CD25loFoxp3+ cells accelerated arthritis and aggravated symptoms. Under arthritis conditions, autoreactive CD4+ T cells are mainly derived from CD25 lo Foxp3 + CD4 + T cells (Fig. 5a-c). In contrast, CD25hiFoxp3+ cells significantly inhibited osteoclastogenesis, almost half of CD25loFoxp3+ cells lost Foxp3 expression, and almost all CD25hiFoxp3+ cells still expressed Foxp3 (Fig. 5d). After stimulation with type II collagen in vitro, CD25loFoxp3+ cells began to proliferate, indicating that they contained more autoreactive T cells (Fig. 5e).
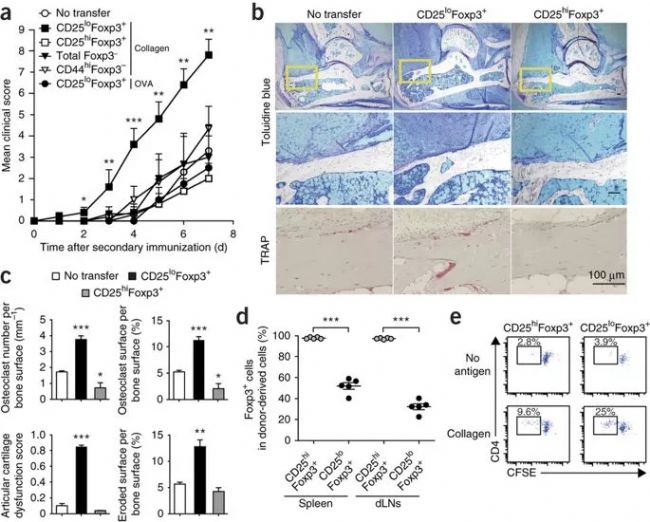
Figure 5. Pathogenic role of exFoxp3 T cells to arthritis in vivo.
Scene: Arthritis
The hero: ex Foxp3 T H 17 cells
I am an ex Foxp3 T H 17 cell, belonging to the pT reg cell tribe, which loses Foxp3 expression from CD25loFoxp3+ CD4+ T cells, aggregates into the joint, and is transformed by IL-6 produced by synovial fibroblasts. The expression of Ccr6, CCL20, IL23R and RANKL is my hallmark and has a strong ability to promote osteoclastogenesis, which plays a key role in the pathology of arthritis. I hope that through my monologue, everyone can understand the mechanism and key role of autoimmune arthritis. I can also become a marker of RA, predict the therapeutic effect of anti-IL-6 antibody, and then develop into a new treatment for autoimmune diseases. .
The authors of this article made full use of genetically edited mice to study the partial mechanisms of autoimmune diseases. I am very honored that the first pot of gold products from the Ooto Saitu rat IL-17a GFP KI mouse has helped the article. If you need to buy this mouse or prepare your own research mouse, please contact us. Oh!
references:
1. Komatsu, N., Okamoto, K., Sawa, S., Nakashima, T., Oh-hora, M., Kodama, T., ... Takayanagi, H. (2013). Pathogenic conversion of Foxp3+ T cells into TH17 cells in autoimmune arthritis. Nature Medicine, 20(1), 62–68.
2. Zhou, X., Jeker, LT, Fife, BT, Zhu, S., Anderson, MS, McManus, MT, & Bluestone, JA (2008). Selective miRNA disruption in T reg cells leads to uncontrolled autoimmunity. Of Experimental Medicine, 205(9), 1983–1991.
3. Zhou, X., Bailey-Bucktrout, SL, Jeker, LT, Penaranda, C., MartÃnez-Llordella, M., Ashby, M., ... Bluestone, JA (2009). Instability of the transcription factor Foxp3 leads to The generation of pathogenic memory T cells in vivo. Nature Immunology, 10(9), 1000–1007.
Acne Pimple Patch,Diy Pimple Patch,Pimple Band Aid,Peace Out Acne Dots
Wenzhou Celecare Medical Instruments Co.,Ltd , https://www.celecaremed.com