Macrophages are the key to helping the heart to repair and even regenerate
December 25, 2018 Source: Ministry of Science and Technology
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];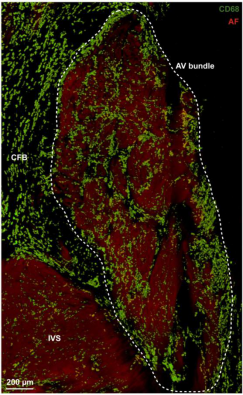
Macrophages in human atrioventricular node (AV), densely interspersed with macrophages (green) around cardiomyocytes (red)
Scientists at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre (PMCC) have identified key types of heart repair and potentially regenerative cells that help heart attacks. These cells are macrophages that can enter a "new" state in which they help the growth and development of organs. This means they can be directed for heart repair after a heart attack.
Macrophages are white blood cells that live in organs. They are a key component of the immune system and they are recognized for their ability to fight infection. Recently, they have been found to promote tissue repair and regeneration.
Dr. Slava Epelman, a cardiologist and immunologist at PMCC, explained: "We are very excited about these findings, which is a reward for the hard work of the past five years. We try to understand how these cells help patients with heart attacks. We Using computational methods, it was found that there were at least four types of macrophages in the uninjured heart, rather than a single type of macrophage, and this number increased to 11 after a heart attack, indicating a behavioral ratio of the immune system. What we imagine is much more complicated."
The study, published in Nature Immunology, helped scientists achieve two important findings.
First, they found that the newborn's macrophages suffered a loss after an adult heart attack. This can explain why an adult heart is not as easy to heal as a newborn's heart. In very young animals, the number of macrophages in the newborn state increases, which is very efficient in triggering cardiac and vascular cell regeneration.
Dr. Epelman explained: "The removal of nascent macrophages by genetic means that the heart function of adult animals is exacerbated after a heart attack. The most severely deteriorating location is where the damaged and undamaged myocardium are separated. This is the only area where the number of macrophages in an adult heart increases, which explains their important role in tissue repair at their location."
They also found that a large number of macrophages were attracted to the heart after a heart attack, and a few entered a new state, but it was too late. Dr. Epelman said: "These cells have the ability to transform into a new state of regeneration, but not fast enough." After a heart attack, when they reach the heart, scars in the myocardial position have formed.
These findings are a very important step for scientists to determine how the heart recovers itself after it has been damaged. Dr. Epelman said: "Every cell in the human body plays a unique role. Our next question is how to more efficiently guide the macrophages entering the heart to a new state, and ultimately achieve more effective heart treatment. method."
Disinfection And Sterilization Equipment
Plasma Air Sterilizer,Plasma Air Sterilizing Machine ,Air Sterilization Purifier,Bio Plasma Air Sterilizers
Foshan Ja Suo Medical Device Co., LTD , https://www.jasuodental.com